Parts of Speech
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. Understanding parts of speech is essential for determining the correct definition of a word when using the dictionary.
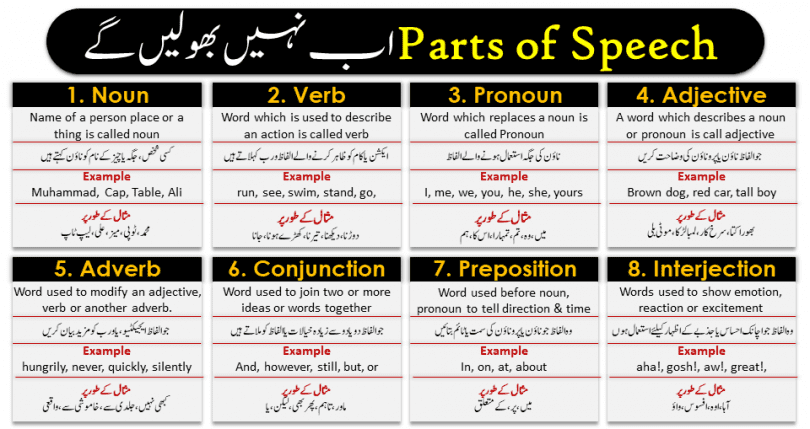
- The Noun (n.)
A noun is a word which gives a name to something, in some cases you might hear them referred to as a ‘naming word.’ There are various different subcategories of nouns such as the proper noun, the collective noun, the possessive noun and the common noun. Each one of these serves a different purpose, let’s look at this a little more closely.
Noun Examples:
Muhammad, Pakistan, pen, New Year, dog, cat, elephant, garden, school, work, music, town, cap, teacher, farmer, Sean, Ali, police officer, coffee, football, danger
Noun example sentences:
- The teacher told the student to work hard.
- Ali is good at English but weak at Arabic.
- The Verb (vb.)
A verb is one of the most important parts of speech and is a word which is used to describe an action. There are three main types of verbs which are detailed below.
Examples:
Walk, is, seem, realize, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, laughed, walk…
Verb Example Sentences:
- Don’t try to run before you can walk.
- Did you kiss anybody?
- Leave me alone!
- The Pronoun (pron.)
A pronoun is one which replaces a noun, and once again there are various different types of pronouns within the English language. Each one is used in a different way, let’s take a look at some examples of this.
Examples:
I, me, we, you, he, she, yours, himself, its, my, that, this, those, us, who, whom
Pronoun example sentences:
- Don’t tell her the truth.
- She tried it herself.
- You can’t blame him for everything.
- The Adjective (adj.)
An adjective is a word which describes a noun or pronoun, there are thousands of adjectives within the English language.
Examples:
Beautiful, seven, cute, second, tall, blue, angry, brave, careful, healthy, little, old, generous, red, smart, two, small, tall, some, good, big, useful, interesting…
Brown dog, red car, tall boy, fat cat, big garden.
Adjective example sentences:
- This is a blue
- The small squirrel ran up the tree.
- During the thunderstorm, we saw some heavy
- My mother has short
- The documentary on TV last night was very
- My son has an impressive collection of toy soldiers.
- The weather is hot and sunny today.
- My vacation was exciting.
- The leaves on that tree are green and large.
- The Adverb (adv.)
An adverb is used to modify, or further explain an adjective, verb or another adverb. They can add more information to a sentence making it clearer and easier for the listener to imagine what is being described in detail. Most of the time, adverbs will end in the letters -ly but there are some exceptions to this rule such as the words very and never.
Examples:
Neatly, in the market, every day, tomorrow, very, badly, fully, carefully, hardly, nearly, hungrily, never, quickly, silently, well, really, almost…
Adverb example sentences:
- This is an extremely attractive photograph.
- I have a very large pet dog.
- My car drives quickly.
- When I am running late for work, I eat my breakfast rapidly.
- The boy is crying loudly.
- She carefully preserved all his letters.
- The Conjunction (conj.)
A conjunction is used as a way of joining two or more ideas or words together. Most commonly you will see the words for, and, not, but, or, yet and so used as a conjunction.
Examples:
And, however, still, but, or, so, after, since, before, either, neither, because, unless…
Conjunction example sentences:
- I will go to the shop but not before I have had something to eat.
- This is a gift for my friend.
- I was tired yet I still went to the gym.
- The Preposition (prep.)
A preposition is used in English to show a relationship between two words or phrases. You might recognize a preposition as being words such as in, before, on, at, to, between etc.
Examples:
In, on, at, about, apropos, according to, after, along, above, except, from, near, of, before, since, between, upon, with, to, after, toward…
Preposition example sentences:
- The cat is sitting on the wall.
- I am going to the salon after my dinner.
- The boy ran along the street for an hour.
- You will find the theatre in the town center.
- I saw that news in the newspapers.
- The Interjection (interj.)
An interjection could also be thought of as a exclamation. They are used to emotion, reaction or excitement and have no grammatical link to anything else within the sentence they appear.
Examples:
Ahem!, aha!, gosh!, aw!, great!, hey!, hi!, hooray!, oh!, yeah!, oops!, phew!, eh!, oh!, ouch!, hi!, well!…
Interjection example sentences:
- Phew! That was a close call.
- Wow! Did you see how big that bird was?
- Oh, I forgot to tell you that I saw your father last week.
- Hooray! You passed your exam!
- Well, what did he say?
- Yeah! She’s going with us tonight!





Leave a Comment