Interjection is one of the Parts of Speech, which is used to express sudden emotions, strong reactions and brief exclamations. These are often one or two-word phrases which convey the sentiments and feelings and interestingly, Interjections are used in such a way in sentences that interjections are not grammatically connected to the rest of sentence. Their main purpose is to add emotions, feelings and reactions in spoken and written language as well. Interjections possess the ability to express a wide range of emotions, feelings, sentiments of joy, anger, frustration or excitement.
Interjections are often considered to be versatile and are used in both formal and informal conversations. Interjections add a beautiful element to the conversations which allows speakers and story tellers to convey their message in effective ways. While we are using the interjections in writing, it has to be kept in mind that in which context and in which tone we are using interjection. So that it should enhance the beauty and effectiveness of the sentence rather than disrupting the overall message.
Note: You cam Download FREE PDF of this Lesson at the bottom of Page.
What is interjection?
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling or to request or demand something. It expresses feelings, emotions, or exclamation like, crying, happiness, laughing, sadness, etc. Examples of interjection are listed below.
Wow! That bird is huge. (Expressing astonishment or amazement)
Uh-oh! I forgot to get gas. (Expressing distress or disappointment)
Oops! I mixed tea with juice. (Acknowledging a mistake or mishap)
Psst! what’s the answer to number four?
Ouch! I sprained my ankle. (Conveying pain or discomfort)
Alas! I couldn’t get the scholarship. (Expressing distress or disappointment)
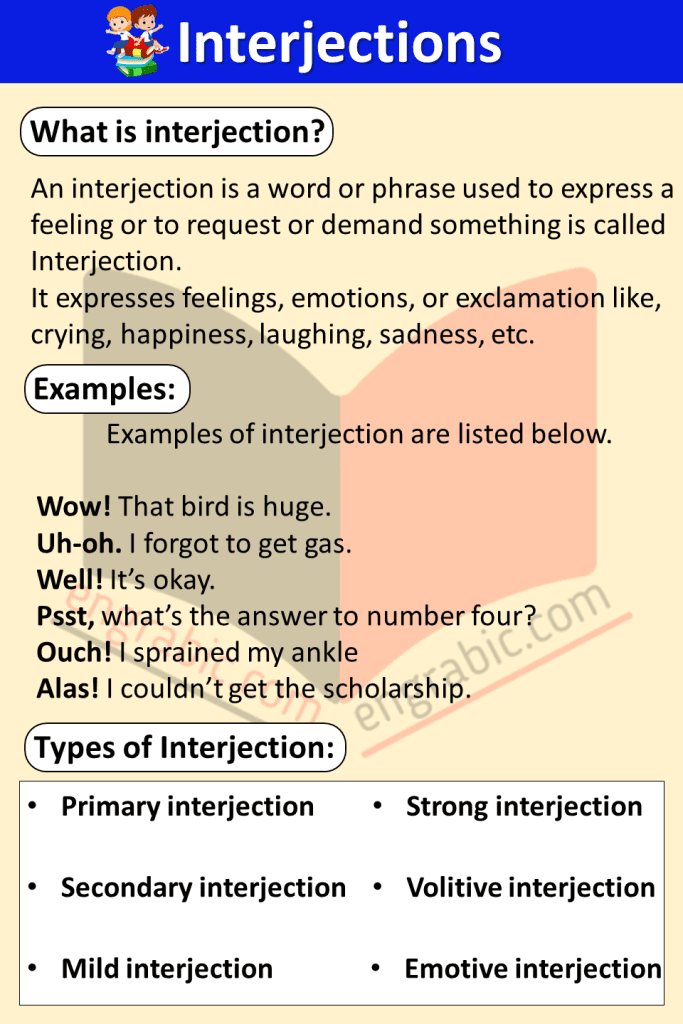

Types of Interjection:
- Primary interjection
- Secondary interjection
- Mild interjection
- Strong interjection
- Volitive interjection
- Emotive interjection
- Emotive interjection
- Cognitive interjection
Lets now discuss each type of interjection with examples below.
- Primary interjection
An interjection is a simple word or phrase that shows your quick feelings or emotions, like surprise, joy, or pain. It’s like an emotional word that stands by itself and doesn’t fit into other groups of words.
Example:
Oh! I am sorry.
- Secondary interjection
Some nouns or adjectives act as interjections which are called secondary interjections, like goodness, indeed, oh my goodness, I mean etc.
Example:
She told him to stop, I mean, it’s really annoying.
- Mild interjection
A mild interjection is a little word or sound that shows a small feeling, like “oh” or “hmm” and “well”.
Example:
Oh! I didn’t know you were coming today.
Hmm! I understand.
Well, I guess we can go to the park if you had like.
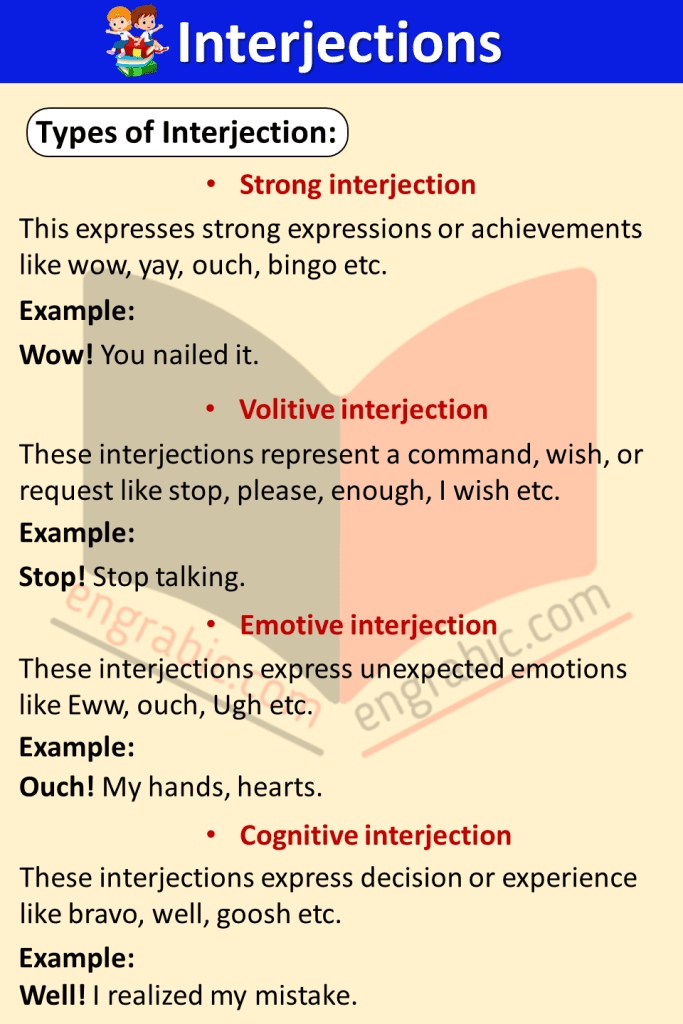
- Strong interjection
This expresses strong expressions or achievements like wow, yay, ouch, bingo etc.
Example:
Wow! You nailed it.
These interjections represent a command, wish, or request like stop, please, enough, I wish etc.


- Volitive interjection
These interjections represent a command, wish, or request like stop, please, enough, I wish etc.
Example:
Stop! Stop talking.
- Emotive interjection
These interjections express unexpected emotions like Eww, ouch, Ugh etc.
Example:
Ouch! My hands, hearts.
- Cognitive interjection
These interjections express decision or experience like bravo, well, goosh etc.
Example:
Well! I realized my mistake.

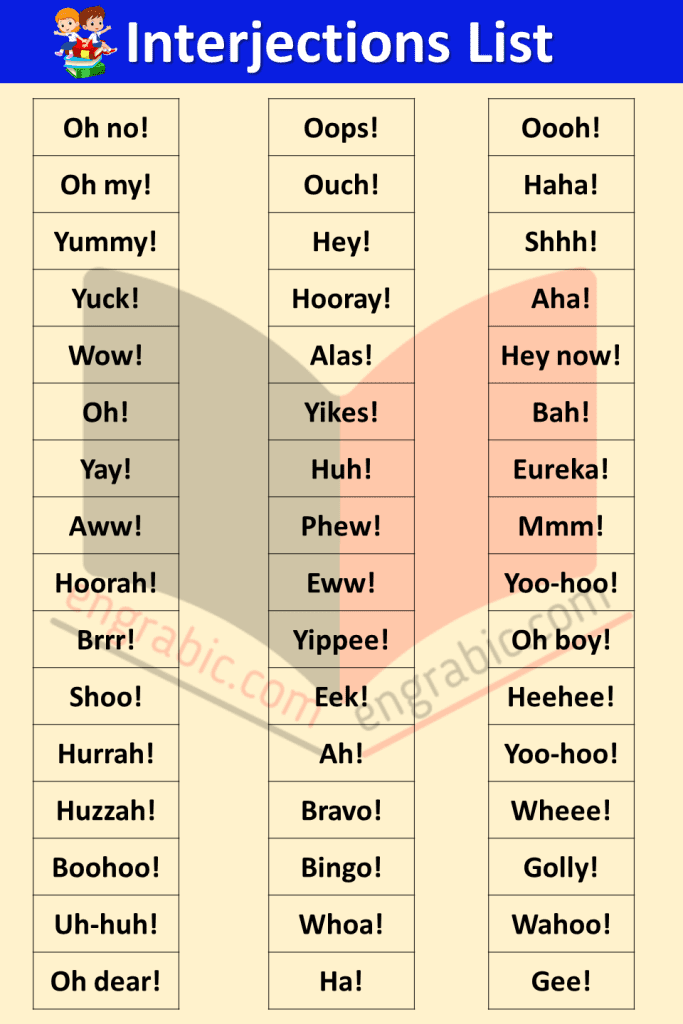
Interjections List
| Oh no! | Oops! | Oooh! |
| Oh my! | Ouch! | Haha! |
| Yummy! | Hey! | Shhh! |
| Yuck! | Hooray! | Aha! |
| Wow! | Alas! | Hey now! |
| Oh! | Yikes! | Bah! |
| Yay! | Huh! | Eureka! |
| Aww! | Phew! | Mmm! |
| Hoorah! | Eww! | Yoo-hoo! |
| Brrr! | Yippee! | Oh boy! |
| Shoo! | Eek! | Heehee! |
| Hurrah! | Ah! | Yoo-hoo! |
| Huzzah! | Bravo! | Wheee! |
| Boohoo! | Bingo! | Golly! |
| Uh-huh! | Whoa! | Wahoo! |
| Oh dear! | Ha! | Gee! |

Download FREE PDF Lesson





Leave a Comment