Pronouns are fundamental component of language that serve a crucial role of replacing a noun in a sentence. The main idea of using pronouns is to simplify communication, avoid repetition and make conversation smooth. Pronouns can refer to people, objects, places, ideas and more, allowing us to express complex ideas and concepts with ease.
Why Pronouns are Important?
Pronouns are like word helpers. They take the place of other words we’ve already talked about, so we don’t have to keep saying the same things. This makes our talking and writing shorter and easier to understand. Pronouns also help connect our ideas, so people can follow along better. They make our talking sound interesting and not boring. Using pronouns correctly is important for making sentences work right. Pronouns can do different jobs in sentences, but they don’t change how sentences work. They help us talk fast when we don’t have a lot of time to chat. So, pronouns are like our language helpers, making talking and writing better!
Pronouns are special words we use to talk about something or someone without saying their name again and again. They make talking and writing easier because we don’t have to keep saying the same word. For example, in the sentence
“She is going to the store,”
The word “she” is a pronoun. It helps us talk about a girl without using her name all the time, which makes our sentences shorter and simpler.
Please Note: You can download FREE PDF at the bottom of page
Given below are subject and object pronouns:
Subject Pronouns:
- I
- You
- He
- She
- It
- We
- They
Object Pronouns:
- Me
- You
- Him
- Her
- It
- Us
- Them
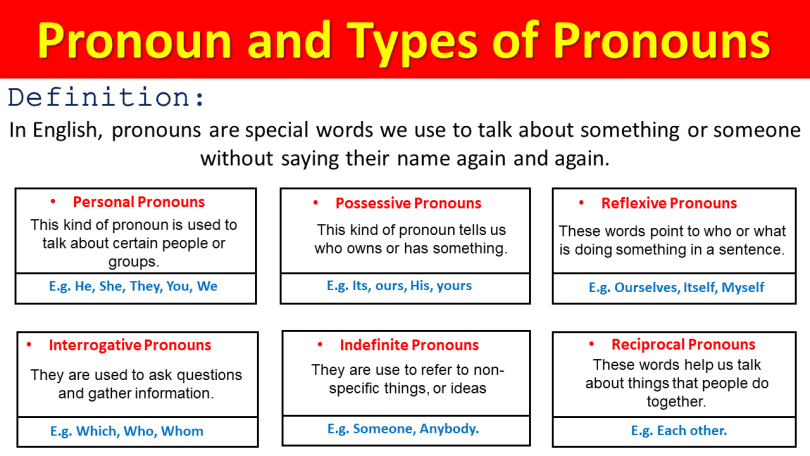
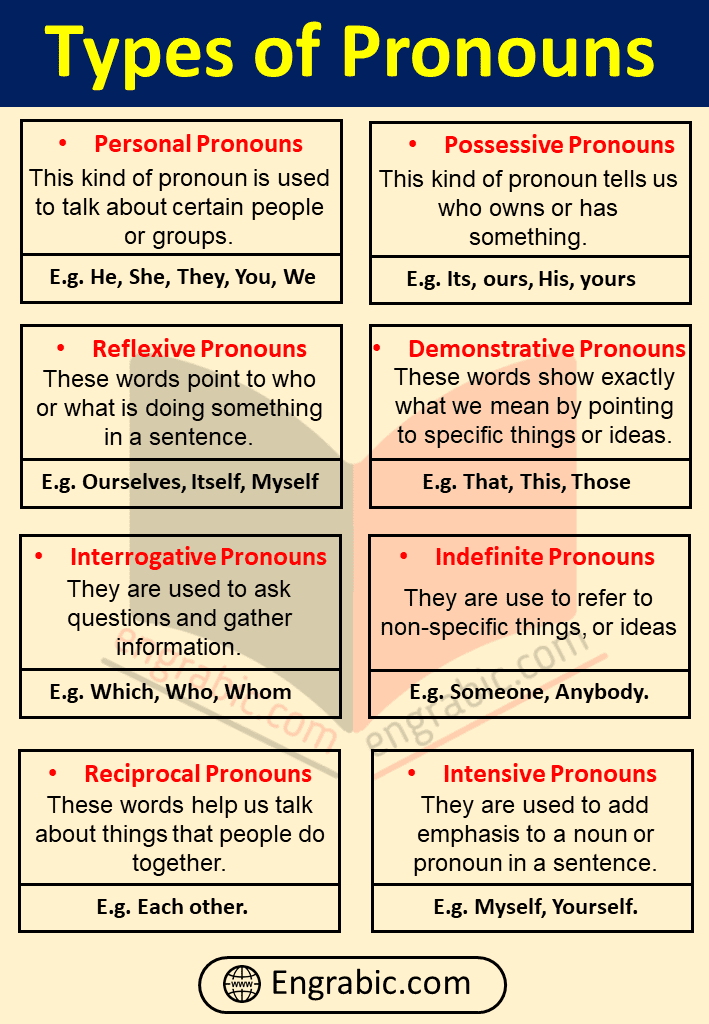
10 Kinds of Pronouns:
- Personal Pronouns
- Possessive Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Relative Pronouns
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Reciprocal Pronouns
- Intensive Pronouns
- Relative Possessive Pronouns
Please Note: You can download FREE PDF at the bottom of page
- Personal Pronouns:
Personal pronouns are special words we use in English to talk about specific people or groups. They take the place of names to make our sentences shorter and not repeat the same words all the time. Personal pronouns can change depending on who we’re talking about, how many there are, and sometimes, whether they are a boy or a girl.
First Person:
- I (singular)
- We (plural)
Second Person:
- You (singular and plural)
Third Person:
- He (singular, masculine)
- She (singular, feminine)
- It (singular, neutral)
- They (plural, can refer to any gender or both genders)
Examples of personal pronouns:
- I – Example: I am happy.
- You – Example: You are my husband.
- He – Example: He is short.
- She – Example: She is naughty.
- It – Example: It is a beautiful car.
- We – Example: We are going to the zoo.
- They – Example: They are my friends.
Please Note: You can download FREE PDF at the bottom of page
- Possessive Pronouns:
Possessive pronouns are special words that tell us who owns something. They’re like a shortcut for words like “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their” when we want to say something belongs to someone. These pronouns can stand by themselves without needing a noun with them. They help us show who has something in a sentence.
- Mine – This car is mine.
- Yours – The red book is yours.
- His – The blue backpack is his.
- Hers – The pink dress is hers.
- Its – The cat is licking its paws.
- Ours – The house is ours.
- Theirs – The bikes are theirs.
- Reflexive Pronouns:
Reflexive pronouns are special words that bounce back to the person or thing doing the action in a sentence. They’re used when that person or thing is both doing and receiving the action. Think of them like a “mirror” that shows the action going back to the same person or thing.
- Myself – I washed myself.
- Yourself – You should believe in yourself.
- Himself – He hurt himself while playing.
- Herself – She dressed herself for the party.
- Demonstrative Pronouns:
We have four special words called demonstrative pronouns: “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.” We use them to point to something we talked about before or something we both understand in our conversation. For instance, when someone says, “Take this,” we don’t know exactly what “this” is, but from our talk, we know what they mean.
- This was my mother’s ring.
- That looks like the car I used to drive.
- These are nice shoes, but they look uncomfortable.
- Those look like riper than the apples on my tree.
- Interrogative Pronouns:
Interrogative pronouns are special words we use to ask questions. There are only five of them, and each has a specific job in asking questions. Some, like “who” and “whom,” are for asking about people. Others can be used to ask about things or people. Once you know these words, you can use them to ask all sorts of questions easily.
- What do you want for your birthday?
- Which shirt do you think looks better on me?
- Who do you think will win the playoff game?
- Whose socks are those?
- Relative Pronouns:
A relative pronoun is a word we use to talk about things we talked about before. It can be people, places, things, animals, or ideas. These pronouns also help us connect two sentences together.
- Who
- Whom
- That
- Which
- Whoever
- Whomever
- Whichever
Please Note: You can download FREE PDF at the bottom of page
- Indefinite Pronouns:
Indefinite pronouns are special words that don’t point to a specific thing, person, or place. They talk about something or someone in a general way, without giving all the details.
- Anybody
- Anyone
- Anything
- Each
- Each one
- Either
- Neither
- Everybody
- Everyone
- Everything
- Nobody
- No one
- Nothing
- Somebody
- Someone
- Something
- Both
- Many
- Few
- All
- Most
- None
- Some
- Intensive Pronouns:
An intensive pronoun is pretty much the same as a reflexive pronoun. It’s a special pronoun that has “self” or “selves” at the end. Its job is to put extra focus on a noun or pronoun we already talked about in the sentence. That’s why we also call them “emphatic pronouns.”
- You can change your body with a good diet and lots of exercise.
- The team understood that they had to do their best on their own.



Leave a Comment