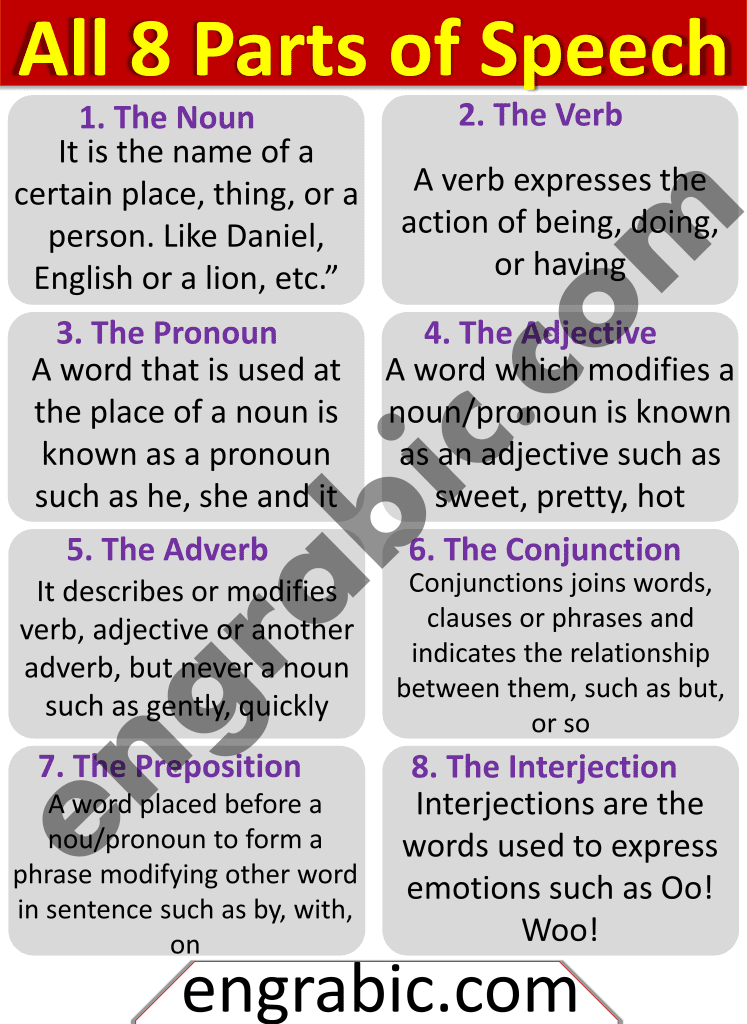
Parts of speech are fundamental categories that classify words based on their grammatical functions, roles, and relationships within sentences. They provide a framework for understanding how words are used in a language and help determine their syntactic behavior. In English, there are eight traditional parts of speech:
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Adjective
- Adverb
- Conjunction
- Verb
- Interjection
- Preposition
1. Noun
“It is the name of a certain place, thing, or a person. Like Daniel, English or a lion, etc.”
There are further two major types of nouns Common nouns and Proper nouns.
- Common noun: The name of a commonplace, non-specific person or a thing is known as a common noun like chair, book, city, etc.
- Proper noun: The name of a special place, person, or thing is known as a proper noun like Allama Muhammad Iqbal, Lahore, etc.
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.
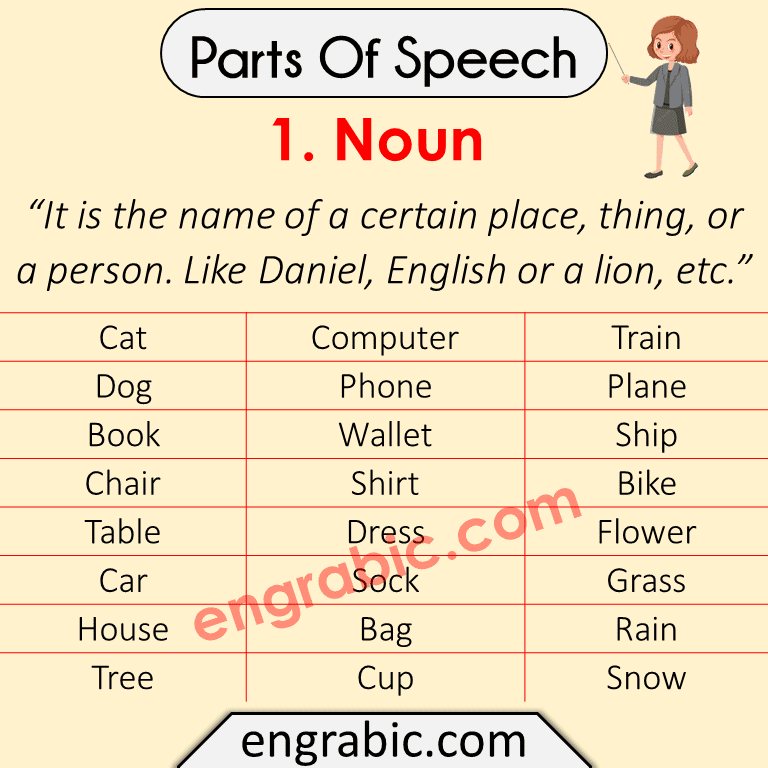

| Cat | Computer | Train |
| Dog | Phone | Plane |
| Book | Wallet | Ship |
| Chair | Shirt | Bike |
| Table | Dress | Flower |
| Car | Sock | Grass |
| House | Bag | Rain |
| Tree | Cup | Snow |
| Flower | Plate | Wind |
| Child | Spoon | Cloud |
| Person | Fork | Fire |
| Country | Knife | Water |
| City | Watch | Air |
| Student | Key | Love |
| Teacher | Window | Hope |
| Mouse | Door | Dream |
| Bird | Table | Idea |
| Fish | Bed | Problem |
| Ball | Lamp | Solution |
| Shoe | Sun | Question |
| Hat | Moon | Answer |
| Apple | Star | Friend |
| Banana | Earth | Family |
| Orange | Sky | Job |
| Chair | Ocean | Money |
| Desk | River | Time |
| Pen | Mountain | Music |
| Pencil | Road | Art |
| Paper | Car | Language |
2. Pronoun
“A word that is used at the place of a noun is known as a pronoun such as he, she and it, etc”
Basically, the pronoun is a word that is usually substituted for a noun. Pronouns are further defined by their type such as
- A personal pronoun refers to a specific person or a thing he, she, it, etc. Parts of speech
- Reflexive pronouns are used to emphasize another noun or a pronoun myself, himself, etc.
- Possessive pronouns indicate ownership of his, her, its, etc.
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.
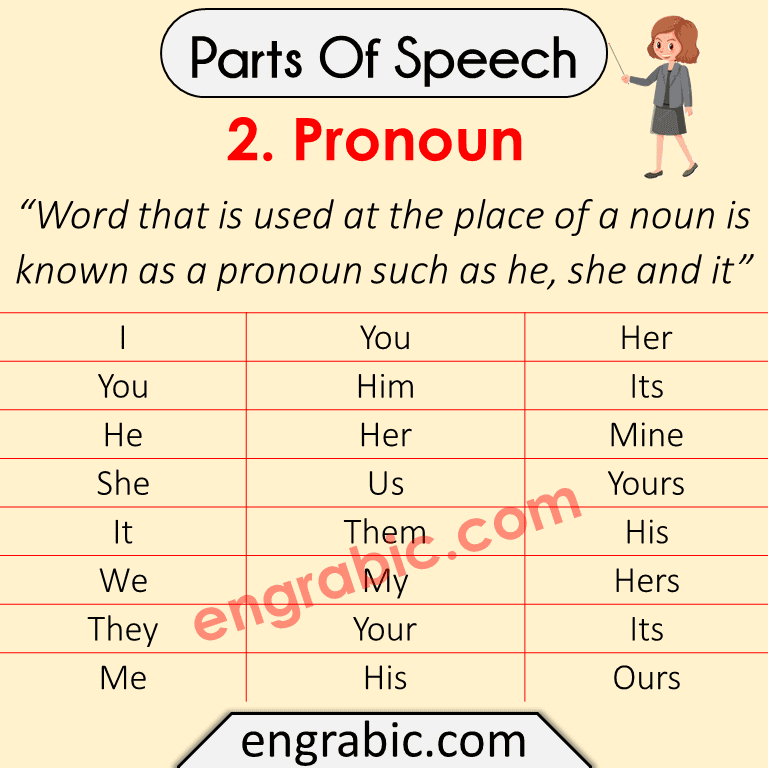

| I | Mine | Myself |
| You | Yours | Yourself |
| He | His | Himself |
| She | Hers | Herself |
| It | Its | Itself |
| We | Ours | Ourselves |
| They | Theirs | Themselves |
| Me | All | Myself |
| You | Both | Yourself |
| Him | Few | Himself |
| Her | Many | Herself |
| Us | Several | Ourselves |
| Them | One | Themselves |
| My | Those | Our |
| Your | Some | Their |
| His | Any | This |
| Her | Every | That |
| Its | None | These |
3. Adjective
“A word which qualifies or modifies a noun or pronoun is known as an adjective such as sweet, pretty, hot, etc.”
- It can also specify the size, quality, and a number of things.
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.
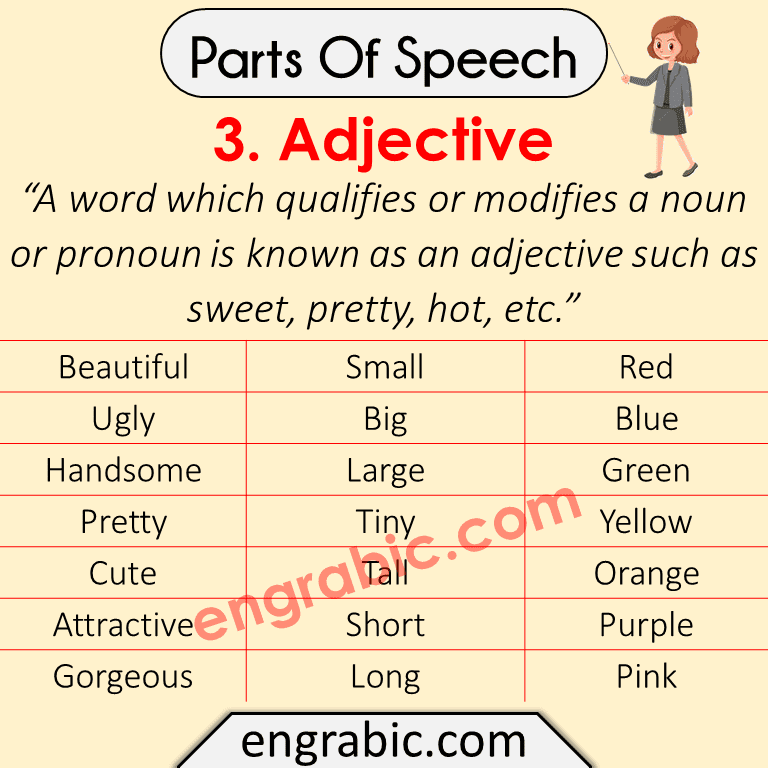

| Beautiful | Small | Red |
| Ugly | Big | Blue |
| Handsome | Large | Green |
| Pretty | Tiny | Yellow |
| Cute | Tall | Orange |
| Attractive | Short | Purple |
| Gorgeous | Long | Pink |
| Stunning | Fat | Brown |
| Elegant | Thin | Black |
| Charming | Narrow | White |
| Graceful | Wide | Gray |
| Smart | Deep | Silver |
| Clever | Shallow | Gold |
| Intelligent | Heavy | Colorful |
| Wise | Light | Dark |
| Dumb | Fast | Bright |
| Brave | Slow | Pale |
| Cowardly | Quick | Pastel |
| Strong | Loud | Vibrant |
| Weak | Quiet | Muted |
| Powerful | Gentle | Neon |
| Feeble | Smooth | Soft |
| Fearless | Rough | Hard |
| Fierce | Sharp | Delicate |
| Calm | Blunt | Bold |
| Aggressive | Pointed | Subtle |
| Friendly | Flat | Vivid |
| Hostile | Round | Faded |
| Happy | Square | Clear |
| Sad | Rectangular | Cloudy |
4. Adverb
It describes or modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb, but never a noun such as gently, quickly, etc.”
- They are usually used to answer the question of when, where, how. They usually end with the word –ly.
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and she quickly disappeared.
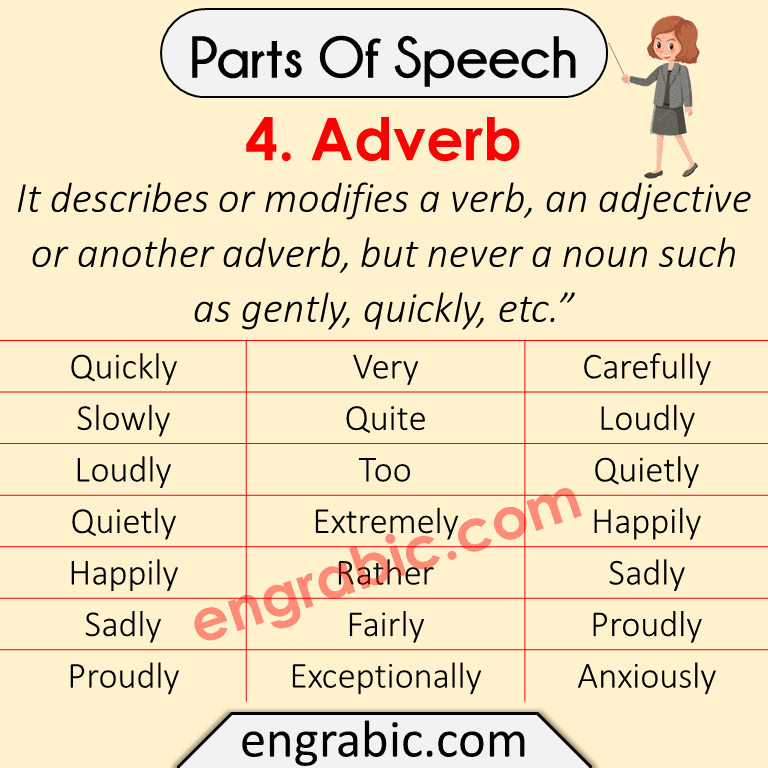

| Quickly | Very | Carefully |
| Slowly | Quite | Loudly |
| Loudly | Too | Quietly |
| Quietly | Extremely | Happily |
| Happily | Rather | Sadly |
| Sadly | Fairly | Proudly |
| Proudly | Exceptionally | Anxiously |
| Anxiously | Incredibly | Nervously |
| Nervously | Terribly | Excitedly |
| Excitedly | Abnormally | Calmly |
| Calmly | Awfully | Joyfully |
| Joyfully | Amazingly | Accurately |
| Accurately | Unusually | Patiently |
| Patiently | Considerably | Generously |
| Generously | Highly | Gently |
| Gently | Moderately | Steadily |
| Steadily | Quite | Firmly |
| Firmly | Remarkably | Smoothly |
| Smoothly | Somewhat | Gracefully |
| Gracefully | Fairly | Directly |
| Directly | Relatively | Freely |
| Freely | Incredibly | Briskly |
| Briskly | Especially | Lazily |
| Lazily | Truly | Lightly |
| Lightly | Particularly | Eagerly |
| Eagerly | Entirely | Politely |
| Politely | Utterly | Rudely |
| Rudely | Remarkably | Swiftly |
| Swiftly | Exceptionally | Steadfastly |
| Steadfastly | Considerably | Heavily |
5. Conjunction
“Conjunctions joins words, clauses or phrases and indicates the relationship between them, such as but, or so, yet are conjunctions.”
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.
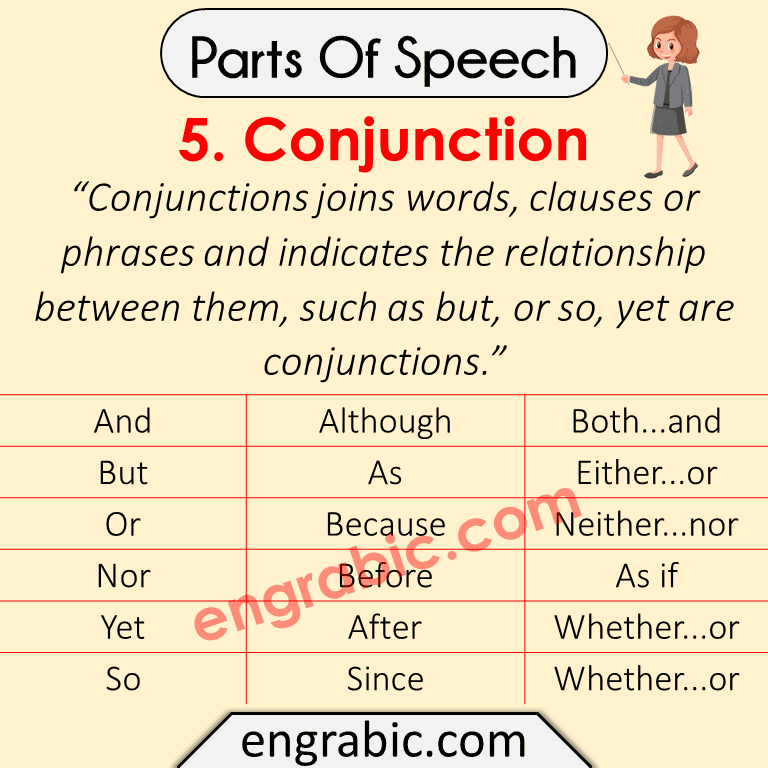

Here is the Examples List of Conjunction:
| And | Although | Both…and |
| But | As | Either…or |
| Or | Because | Neither…nor |
| Nor | Before | Not only…but also |
| Yet | After | Whether…or |
| So | Since | Whether…or |
| For | When | Both…and |
| While | Whenever | Neither…nor |
| As | Where | Not only…but also |
| Just as | If | Either…or |
| Provided that | Unless | Whether…or |
| Since | In case | Both…and |
| Unless | Though | Neither…nor |
| Although | Even if | Not only…but also |
| Even though | As if | Whether…or |
| Whereas | Until | Both…and |
| But | Once | Neither…nor |
| Whether | While | Not only…but also |
| Whether or not | Since | Either…or |
| And | Before | Whether…or |
| Or | After | Both…and |
| Nor | Because | Neither…nor |
| Yet | When | Not only…but also |
| So | Although | Whether…or |
| For | As | Either…or |
| But | If | Whether…or |
| So that | Unless | Both…and |
| In order that | In case | Neither…nor |
| Provided that | Even if | Not only…but also |
| Since | As if | Whether…or |
6. Verb
A verb expresses the action of being, doing, or having.”
- There is a main verb in a sentence and sometimes one or more helping verbs. Such as ( she can sing. Here sing is the main verb and can be a helping verb)
For Example, An old woman brought me a very long dress from a tailor, and then she quickly disappeared.


Here is the Examples List of Verbs:
| Ask | Drive | Play |
| Jump | Read | Sing |
| Talk | Dance | Sleep |
| Write | Swim | Run |
| Study | Cook | Eat |
| Listen | Love | Draw |
| Laugh | Cry | Think |
| Stand | Speak | Work |
| Climb | Watch | Help |
| Smile | Clean | Fly |
| Listen | Give | Take |
| Learn | Open | Close |
| Create | Break | Fix |
| Teach | Call | Cut |
| Paint | Meet | Start |
| Finish | Visit | Drive |
| Buy | Sell | Play |
| Drink | Understand | Sing |
| Write | Dance | Sleep |
| Study | Cook | Eat |
| Listen | Love | Draw |
| Laugh | Cry | Think |
| Stand | Speak | Work |
| Climb | Watch | Help |
| Smile | Clean | Fly |
| Listen | Give | Take |
| Learn | Open | Close |
| Create | Break | Fix |
| Teach | Call | Cut |
| Paint | Meet | Start |
| Finish | Visit | Drive |
| Buy | Sell | Play |
7. Interjection
“Interjections are the words used to express emotions such as Oo! Woo! Etc.”
It is often followed by the sign of exclamation.
Examples:
- Oh my!
- Hurrah! We won the match.
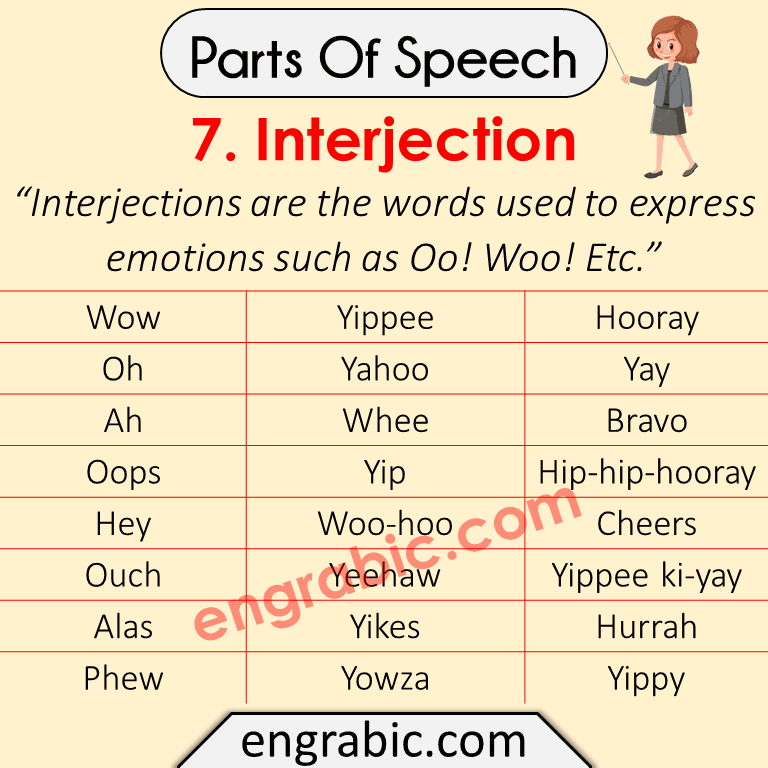

Here is the Examples List of Interjections:
| Wow | Yippee | Hooray |
| Oh | Yahoo | Yay |
| Ah | Whee | Bravo |
| Oops | Yip | Hip-hip-hooray |
| Hey | Woo-hoo | Cheers |
| Ouch | Yeehaw | Yippee ki-yay |
| Alas | Yikes | Hurrah |
| Phew | Yowza | Yippy |
| Huh | Woohoo | Yee |
| Oh no | Yesss | Yaaay |
| Ahem | Yodel | Yip-yip |
| Eek | Yummy | Woo |
| Eureka | Yabba dabba doo | Yeeh |
| Darn | Wowzers | Yoho |
| Gosh | Yessir | Yow |
| Hooray | Yayyy | Yoo-hoo |
| Oops | Yippee | Huzzah |
8. Preposition
A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence such as by, with, on, etc”
Examples:
- The book is on the table.
- He wrote a letter with the blue pen.
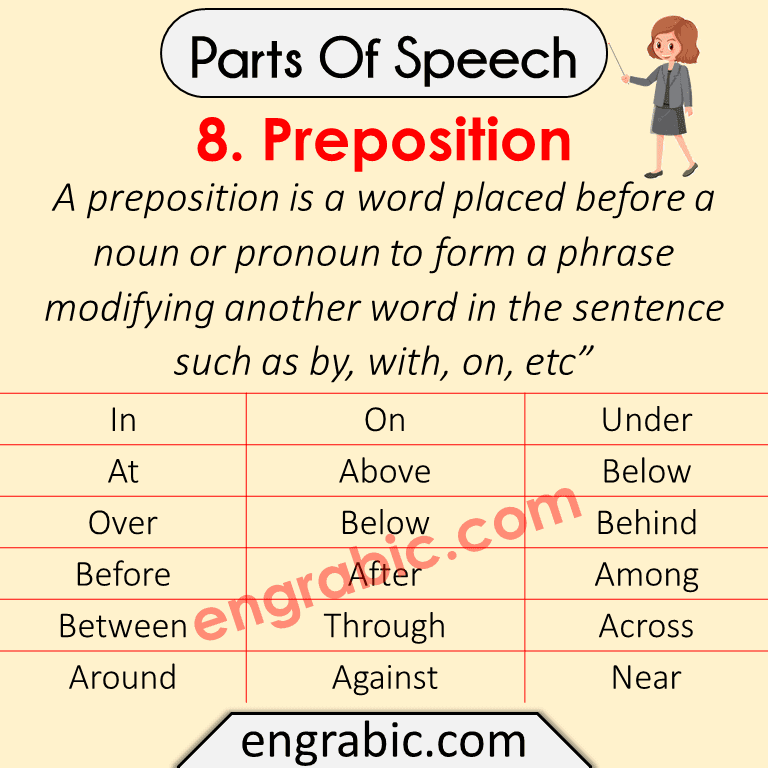

Here is the Examples List of Prepositions:
| In | On | Under |
| At | Above | Below |
| Over | Below | Behind |
| Before | After | Among |
| Between | Through | Across |
| Around | Against | Near |
| Beside | From | To |
| Into | Onto | Within |
| Without | Toward | Upon |
| With | Amongst | Inside |
| Outside | Amid | About |
| During | Until | Upon |
| Like | Unlike | For |
| Since | By | Behind |
| Over | Past | Throughout |
| Except | Beside | With |
| Without | Amongst | Against |
| Near | Above | Underneath |
| In front of | Opposite | Across from |
| Next to | Along | Behind |
| Below | Around | Within |
| By | Among | Alongside |
| Toward | Between | Upon |
| Inside | Outside | Despite |
| With | Upon | Along |
| Up | Down | Throughout |
| For | During | Behind |
| By | Near | Beneath |







Leave a Comment